| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by IbilibiOgada: 5:33pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Lol
They won't eat this one. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by VajanahDischaj(f): 5:34pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
see heavy lies!!blogger wey dey find traffic!
wey the blood for the bori? |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by claremont(m): 5:34pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Hammer-Headed Bat. 2 Likes 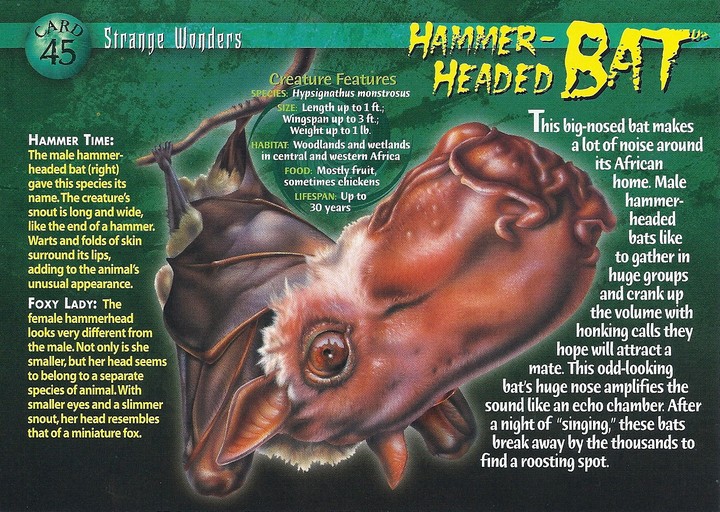
|
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by LockDown69(m): 5:34pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
this your english sha... Hmmm. Strange bat-like creature. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by larabae13(f): 5:34pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Some pple will be saying d bat is an evil spirit lyk dat...ishe aye  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by nurex01(m): 5:34pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Ewo |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by KakiP(m): 5:36pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Thanks for enlightening us, before people will start thinking otherwise bluaero:
That's a hammer-headed bat.
Very likely to be a male, due to the size of it's head for producing very loud honking calls to attract mate.
Trust our people to quickly call it a winsh  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by ruggedtimi(m): 5:36pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Spectre bat |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Sanchez01: 5:37pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Nigerians and superstition. It's a hammerheaded bat. Below are pictures culled from Google Images. 2 Likes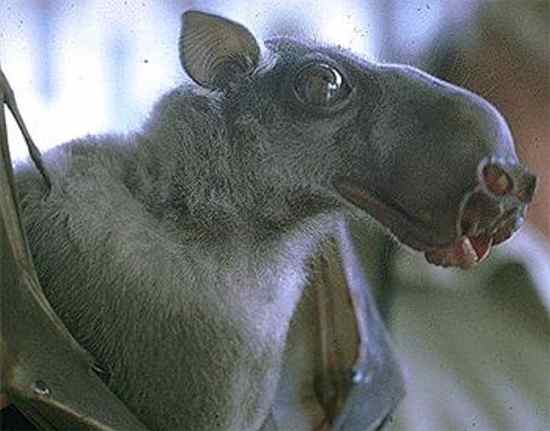 

|
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by egedege1(m): 5:37pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
This is spiritual  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by LockDown69(m): 5:37pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Looks like a mutated bat. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by nwabuwa: 5:41pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Usu ohu imi.. Bat with plenty nose,, makes terrifying noise at night, still edible... 1 Like |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Nobody: 5:41pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
mesoprogress:
Rabid bat. It might have rabies, hence flying in the day. Any person bitten should see a doctor ASAP for anti rabies vaccine.
Hmmn, the nose. Looks familiar, hope it's not lie mohammed. Rabid bats are only found on the Central and South American continent. The bats in Nigeria do not bite humans or animals. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by moshould(m): 5:43pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
I suspect ikpeazu a ogah....let's consult d oracle....ogbakri |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by annnikky(f): 5:44pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
D head of bat dey fear no be small, if this one c u for nyt ur name na sori  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Nobody: 5:45pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
bluaero:
That's a hammer-headed bat.
Very likely to be a male, due to the size of it's head for producing very loud honking calls to attract mate.
Trust our people to quickly call it a winsh  Hammer Headed or Big-lipped Bat. Hypsignathus monstrosus. Don't mind Nigerians and their ignorance. We don't think and reason. We react from false information and wrong ideas which we have taken in for a very very long time. Ignorance Transferred from one generation to another. When we cannot explain a thing we do not choose to study and understand it. We take the LAZY way out and say it is supernatural-witches, wizard, spirits, ghosts, devil, God, gods, juju, etc. 1 Like |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by bigfather(m): 5:45pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
But the thing ugly sha |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by admax(m): 5:47pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
You were faster than me.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hammer-headed_ba.shortgun:
The hammer-headed bat (Hypsignathus monstrosus), also known as the big-lipped bat , is a megabat widely distributed in equatorial
Africa . This large bat is found in riverine forests, mangroves , swamps , and palm forests at elevations less than 1,800 metres (5,900 ft).
Taxonomy
The hammer-headed bat is a member of the family Pteropodidae . Pteropodidae is divided into two subfamilies, Macroglossinae which contains six genera, and Pteropodinae containing thirty-six genera including
Hypsignathus . The family Pteropodidae is found within the suborder, Megachiroptera . This group is commonly referred to as the megabats or flying foxes.
Physical description
The hammer-headed bat is the largest bat in Africa with a wingspan of 686 to 970 mm (27.0 to 38.2 in) and a total length of 195 to 285 mm (7.7 to 11.2 in). Males, ranging from 228 to 450 g (8.0 to 15.9 oz), are significantly larger than females, which range from 218 to 377 g (7.7 to 13.3 oz). [2][3]
Pelage is grey-brown to slaty-brown with a whitish collar of fur extending from shoulder to shoulder. [4] The flight membranes are brown and the ears are dark brown with a tuft of white fur at the base. The face is dark brown with a few long, stiff whiskers around the mouth.
The skull may be diagnosed by specific dental features. The second premolar and molars are markedly lobed. This feature is specific for this genus, and no other African fruit bats have this characteristic.
There is extreme sexual dimorphism in this species. [5] The male possesses an enormous head for producing loud honking calls. [5] The enlarged rostrum, larynx and lips allow these sounds to be extremely resonant. The larynx is one half the length of the vertebral column and fills out most of the thoracic cavity. It is nearly three times larger in males than females. The male also has a hairless split chin and warty rostrum with wrinkled skin around it. Females have a much more fox-like appearance similar to most fruit bats. [4]
Ecology and behavior
Hammer-headed bats are frugivores . Figs make up much of their diet, but they may also include
mangos, bananas and guavas . There are some complications inherent in a fruit diet such as insufficient protein intake. It is suggested that fruit bats compensate for this by possessing a proportionally longer intestine compared to
insectivorous species. [4] This enhances their ability to absorb protein. They also have very rapid digestive systems allowing these bats to assimilate high amounts of fruit to ensure that adequate protein is absorbed. It is also suggested that by eating a wide variety of fruits with varying protein contents, fruit bats are able to maintain an entirely frugivorous diet.[6]
Generally fruit is picked and taken to a nearby tree where it is chewed, the juice squeezed out and the pulp discarded. Since they often do not consume the pulp, these bats are not considered to be good seed distributors. [7] Males may forage long distances (up to 10 km or 6 mi) to locate the highest quality food. Females rely on established feeding routes that offer a constant supply of lower quality food. This may reflect different metabolic requirements based on body size differences.
Large bats often experience difficulties with overheating during flight. The limited thermoregulatory capabilities of flying bats appears to be one factor closely associated with why flight activity primarily occurs during cooler nocturnal temperatures. It has been found that hammer-headed bats are able to tolerate higher ambient temperatures during flight than other bats. [8] This ability is associated with this bat’s high thermal conductance (C f ) which is defined as the total heat loss less the heat loss due to evaporation divided by body temperature less the ambient temperature (C f = [H 1 – He ]/[T b – T a ]). However, they are especially sensitive to ambient temperatures below 11 °C (52 °F) and a decrease in flight coordination is seen. Due to the large surface area of the wing, convective heat loss to cool air may be significant enough to chill flight muscles preventing the precise coordination essential for flight.
These bats are nocturnal, roosting during the day in the forest canopy . They rely on camouflage to hide them from predators. [4] Specific species of trees are not selected for roosting, however some roosts may be used for long periods of time. Roosts are generally 20–30 metres (70–100 ft) from the ground.
The main predators of this species are humans and nocturnal and diurnal birds of prey. However, infection by parasites is often the most significant problem for the hammer-headed bat. Adults are often infected with mites and the hepatoparasite, Hepatocystis carpenteri.
Reproduction and mortality
Little is known about reproduction in hammer-headed bats. In some populations breeding is thought to take place semi-annually during the dry seasons. The timing of the dry season varies depending on the locality, but in general there are two breeding seasons, one from June to August and the other from December to February. [4] However, in other populations, breeding is not restricted to dry seasons and occurs during all months of the year.
This species is often cited as a classic model of lek mating. [9] In this type of mating system, males cluster in dense groups at specific locations known as mating arenas. [9] In some populations of hammer-headed bats, males gather along rivers at night and display by rapid wing flapping accompanied by loud vocalizations. [10] An arena may contain from 25 to 132 males. Females fly through the arena assessing the males. Once the female’s choice is made, the female lands on the branch and sits beside the male. Once chosen, the male emits a buzzing call and copulation ensues.
However, some populations of hammer-headed bats do not use the lek mating strategy. Males actively display but are not found clustering in groups. [11] This species is highly polygamous . Some estimates suggest that as few as six percent of the males in a population account for up to seventy-nine percent of the matings.
Females generally produce one offspring at a time. Neither gestation nor time until weaning have been reported for this species. Females mature more quickly than males and are sexually mature after six months. They continue to grow and reach adult size at nine months. Males do not reach sexual maturity until approximately eighteen months of age and they do not obtain their unique facial morphology until twelve months. Compared with other bats, this bat is rather long-lived with an average life expectancy of thirty years in the wild.
Interactions with humans
H. monstrosus has no special conservation status. In 2004, the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species listed this species as LC (least concern) on the basis of its widespread distribution and lack of threats to its habitat. [1]
Due to this bat’s diet of fruit, it may be considered a crop pest. It has also been observed to attack live chickens. [12] This observation was reported once and cannot be considered a regular occurrence. Humans hunt this large bat and consume it as bushmeat.
The hammer-headed bat is one of three species of African fruit bat that are thought to serve as reservoirs for the Ebola virus.[13] Anti-ebolavirus antibodies and viral RNA have been isolated from all three. However, isolation of viral RNA has not been repeated. It is not known whether these species are incidental hosts or a reservoir of Ebolavirus infection for humans and other terrestrial mammals. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Aroh48(m): 5:47pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
sogy2:
This is purely the hands of God at work. I learnt a lesson from the Europ Cup Final.1.It doesn't matter who you know or what you have before God can Bless you. 2. Weeping don't last all days. 3. God has the capacity to turn things around at any point in time. everything,una go turn am to preaching.u dey vex? 1 Like |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Guyman02: 5:47pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
bluaero:
That's a hammer-headed bat.
Very likely to be a male, due to the size of it's head for producing very loud honking calls to attract mate.
Trust our people to quickly call it a winsh  Before nko, what do expect. If you tell them it is hammer headed bat they will say you be small pikin. But you need to realize that this particular bat species is one of the 3 fruit bats in Africa that carry the Ebola virus, without showing any symptoms. Not only are they huge but they can also be deadly! 
|
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Omeny: 5:48pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
This one na Ibo made nau.
I trust my Ibo brothers, them too much.
Nothing we no fit convert ooo. |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by smart2008: 5:49pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
|
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Orikinla(m): 5:49pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
mesoprogress:
Rabid bat. It might have rabies, hence flying in the day. Any person bitten should see a doctor ASAP for anti rabies vaccine.
Hmmn, the nose. Looks familiar, hope it's not lie mohammed.  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Situation001(m): 5:49pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
|
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by emperorchedda(m): 5:54pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Had it been this happened in Edo it would have been called winsh  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Alberto44(m): 5:55pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
whizjay:
It's obviously species of bat...
Birds have beaks and feathers...
 but since it's onitsha...
What can I say!? but since it's onitsha...
What can I say!?
Abi ooo |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Nobody: 5:56pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
hmmmmm...I cnt see where the bullet penetrated d bat ooo.....
Anyway d thing worwo sha.... |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by VictorRomanov: 5:57pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
They just killed this cute bat for nothing? Chai! |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by 4reala(m): 5:57pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
cnwokike:
Chaiii. You see what government has caused?
@lalasticlala, mynd44, seun come and see.
4reala, i know you have a comment for these people. lol, dat na some pple food o  |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Nokio1: 5:57pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
First time ever on NL
some killed an animal
Without roasting it. 1 Like 1 Share |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by Guyman02: 5:59pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Nokio1:
First time ever on NL
some killed an animal
Without roasting it. This specie of bat carries the Ebola virus and should not be eaten |
| Re: Bat Shot Dead In An Office In Onitsha, Anambara State by stanisbaratheon: 6:01pm On Jul 11, 2016 |
Haaaaaaa 'senior man' you just copy wikipedia come drop for here. You be highest  shortgun:
The hammer-headed bat (Hypsignathus monstrosus), also known as the big-lipped bat , is a megabat widely distributed in equatorial
Africa . This large bat is found in riverine forests, mangroves , swamps , and palm forests at elevations less than 1,800 metres (5,900 ft).
Taxonomy
The hammer-headed bat is a member of the family Pteropodidae . Pteropodidae is divided into two subfamilies, Macroglossinae which contains six genera, and Pteropodinae containing thirty-six genera including
Hypsignathus . The family Pteropodidae is found within the suborder, Megachiroptera . This group is commonly referred to as the megabats or flying foxes.
Physical description
The hammer-headed bat is the largest bat in Africa with a wingspan of 686 to 970 mm (27.0 to 38.2 in) and a total length of 195 to 285 mm (7.7 to 11.2 in). Males, ranging from 228 to 450 g (8.0 to 15.9 oz), are significantly larger than females, which range from 218 to 377 g (7.7 to 13.3 oz). [2][3]
Pelage is grey-brown to slaty-brown with a whitish collar of fur extending from shoulder to shoulder. [4] The flight membranes are brown and the ears are dark brown with a tuft of white fur at the base. The face is dark brown with a few long, stiff whiskers around the mouth.
The skull may be diagnosed by specific dental features. The second premolar and molars are markedly lobed. This feature is specific for this genus, and no other African fruit bats have this characteristic.
There is extreme sexual dimorphism in this species. [5] The male possesses an enormous head for producing loud honking calls. [5] The enlarged rostrum, larynx and lips allow these sounds to be extremely resonant. The larynx is one half the length of the vertebral column and fills out most of the thoracic cavity. It is nearly three times larger in males than females. The male also has a hairless split chin and warty rostrum with wrinkled skin around it. Females have a much more fox-like appearance similar to most fruit bats. [4]
Ecology and behavior
Hammer-headed bats are frugivores . Figs make up much of their diet, but they may also include
mangos, bananas and guavas . There are some complications inherent in a fruit diet such as insufficient protein intake. It is suggested that fruit bats compensate for this by possessing a proportionally longer intestine compared to
insectivorous species. [4] This enhances their ability to absorb protein. They also have very rapid digestive systems allowing these bats to assimilate high amounts of fruit to ensure that adequate protein is absorbed. It is also suggested that by eating a wide variety of fruits with varying protein contents, fruit bats are able to maintain an entirely frugivorous diet.[6]
Generally fruit is picked and taken to a nearby tree where it is chewed, the juice squeezed out and the pulp discarded. Since they often do not consume the pulp, these bats are not considered to be good seed distributors. [7] Males may forage long distances (up to 10 km or 6 mi) to locate the highest quality food. Females rely on established feeding routes that offer a constant supply of lower quality food. This may reflect different metabolic requirements based on body size differences.
Large bats often experience difficulties with overheating during flight. The limited thermoregulatory capabilities of flying bats appears to be one factor closely associated with why flight activity primarily occurs during cooler nocturnal temperatures. It has been found that hammer-headed bats are able to tolerate higher ambient temperatures during flight than other bats. [8] This ability is associated with this bat’s high thermal conductance (C f ) which is defined as the total heat loss less the heat loss due to evaporation divided by body temperature less the ambient temperature (C f = [H 1 – He ]/[T b – T a ]). However, they are especially sensitive to ambient temperatures below 11 °C (52 °F) and a decrease in flight coordination is seen. Due to the large surface area of the wing, convective heat loss to cool air may be significant enough to chill flight muscles preventing the precise coordination essential for flight.
These bats are nocturnal, roosting during the day in the forest canopy . They rely on camouflage to hide them from predators. [4] Specific species of trees are not selected for roosting, however some roosts may be used for long periods of time. Roosts are generally 20–30 metres (70–100 ft) from the ground.
The main predators of this species are humans and nocturnal and diurnal birds of prey. However, infection by parasites is often the most significant problem for the hammer-headed bat. Adults are often infected with mites and the hepatoparasite, Hepatocystis carpenteri.
Reproduction and mortality
Little is known about reproduction in hammer-headed bats. In some populations breeding is thought to take place semi-annually during the dry seasons. The timing of the dry season varies depending on the locality, but in general there are two breeding seasons, one from June to August and the other from December to February. [4] However, in other populations, breeding is not restricted to dry seasons and occurs during all months of the year.
This species is often cited as a classic model of lek mating. [9] In this type of mating system, males cluster in dense groups at specific locations known as mating arenas. [9] In some populations of hammer-headed bats, males gather along rivers at night and display by rapid wing flapping accompanied by loud vocalizations. [10] An arena may contain from 25 to 132 males. Females fly through the arena assessing the males. Once the female’s choice is made, the female lands on the branch and sits beside the male. Once chosen, the male emits a buzzing call and copulation ensues.
However, some populations of hammer-headed bats do not use the lek mating strategy. Males actively display but are not found clustering in groups. [11] This species is highly polygamous . Some estimates suggest that as few as six percent of the males in a population account for up to seventy-nine percent of the matings.
Females generally produce one offspring at a time. Neither gestation nor time until weaning have been reported for this species. Females mature more quickly than males and are sexually mature after six months. They continue to grow and reach adult size at nine months. Males do not reach sexual maturity until approximately eighteen months of age and they do not obtain their unique facial morphology until twelve months. Compared with other bats, this bat is rather long-lived with an average life expectancy of thirty years in the wild.
Interactions with humans
H. monstrosus has no special conservation status. In 2004, the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species listed this species as LC (least concern) on the basis of its widespread distribution and lack of threats to its habitat. [1]
Due to this bat’s diet of fruit, it may be considered a crop pest. It has also been observed to attack live chickens. [12] This observation was reported once and cannot be considered a regular occurrence. Humans hunt this large bat and consume it as bushmeat.
The hammer-headed bat is one of three species of African fruit bat that are thought to serve as reservoirs for the Ebola virus.[13] Anti-ebolavirus antibodies and viral RNA have been isolated from all three. However, isolation of viral RNA has not been repeated. It is not known whether these species are incidental hosts or a reservoir of Ebolavirus infection for humans and other terrestrial mammals. |







 but since it's onitsha...
What can I say!?
but since it's onitsha...
What can I say!?